Liberation Of Europe on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The final battle of the European Theatre of World War II continued after the definitive overall surrender of Nazi Germany to the
The final battle of the European Theatre of World War II continued after the definitive overall surrender of Nazi Germany to the
 Liberation of Nazi concentration camps and refugees: Allied forces began to discover the scale of the Holocaust, confirming the findings of Pilecki's 1943 Report. The advance into Germany uncovered numerous Nazi concentration camps and forced labour facilities. Up to 60,000 prisoners were at Bergen-Belsen when it was liberated on 15 April 1945, by the British
Liberation of Nazi concentration camps and refugees: Allied forces began to discover the scale of the Holocaust, confirming the findings of Pilecki's 1943 Report. The advance into Germany uncovered numerous Nazi concentration camps and forced labour facilities. Up to 60,000 prisoners were at Bergen-Belsen when it was liberated on 15 April 1945, by the British
United States Holocaust Memorial Museum. Four days later troops from the American 42nd Infantry Division found
 Hitler dies by suicide: On 30 April 1945, as the Battle of Nuremberg and the Battle of Hamburg ended with American and British occupation, in addition to the
Hitler dies by suicide: On 30 April 1945, as the Battle of Nuremberg and the Battle of Hamburg ended with American and British occupation, in addition to the
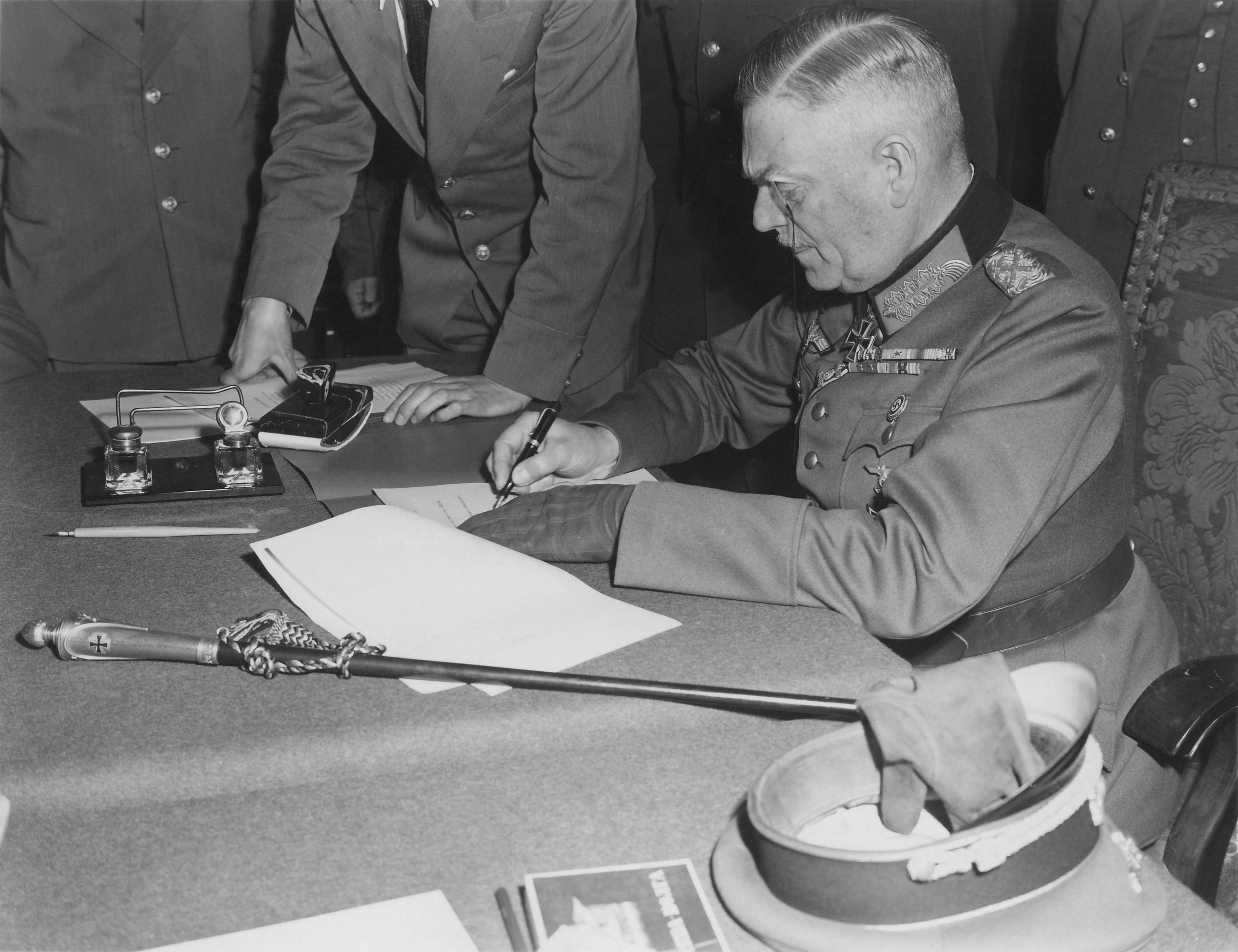
Field Marshal Keitel's surrender
' BBC additional comment b
Peter ŌĆō WW2 Site Helper
/ref> German forces in Bavaria surrender: At 14:30 on 5 May 1945, General Hermann Foertsch surrendered all forces between the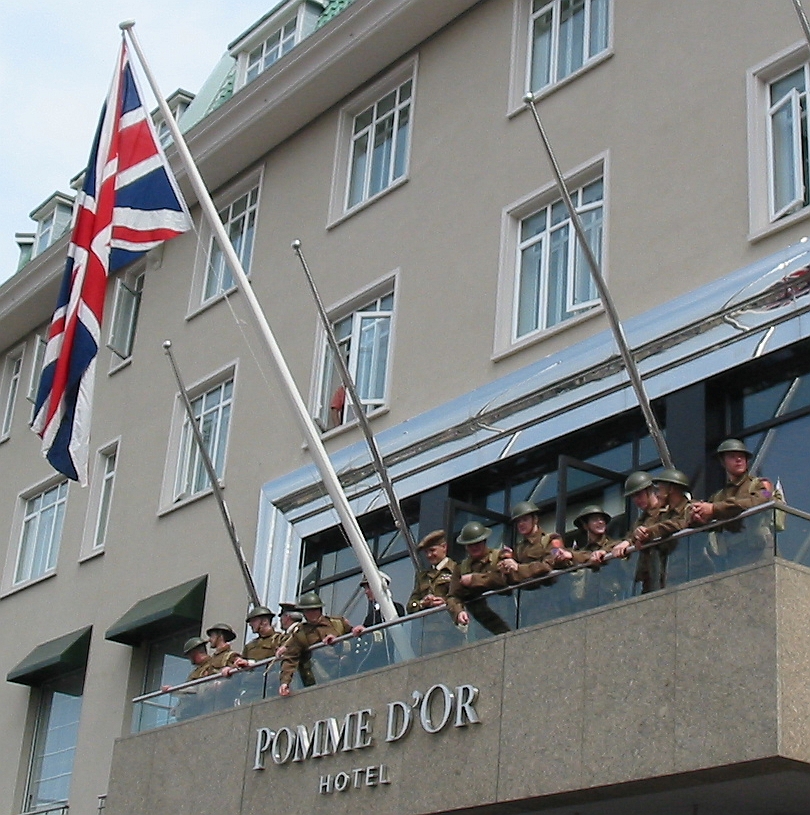 Channel Islanders were informed about the German surrender after: At 10:00 on 8 May, the
Channel Islanders were informed about the German surrender after: At 10:00 on 8 May, the
RAF Site Diary 7/8 May
At 02:41 on the morning of 7 May, at SHAEF headquarters in Reims, France, the chief-of-staff of the German Armed Forces High Command, General Alfred Jodl, signed an unconditional surrender document for all German forces to the Allies. General Franz B├Čhme announced the unconditional surrender of German troops in Norway on 7 May. It included the phrase "All forces under German control to cease active operations at 2301 hours Central European Time on May 8, 1945." The next day, Field Marshal Wilhelm Keitel and other German OKW representatives travelled to Berlin, and shortly before midnight signed another document of unconditional surrender, again surrendering to all the Allied forces, this time in the presence of Marshal Georgi Zhukov and representatives of SHAEF. The signing ceremony took place in a former German Army Engineering School in the Berlin district of
 The final battle of the European Theatre of World War II continued after the definitive overall surrender of Nazi Germany to the
The final battle of the European Theatre of World War II continued after the definitive overall surrender of Nazi Germany to the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
, signed by Field marshal Wilhelm Keitel on 8 May 1945 in Karlshorst
Karlshorst (, ; ; literally meaning ''Karl's nest'') is a locality in the borough of Lichtenberg in Berlin. Located there are a harness racing track and the Hochschule f├╝r Technik und Wirtschaft Berlin (''HTW''), the largest University of Applied ...
, Berlin. After German dictator Adolf Hitler's suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Mental disorders (including depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, personality disorders, anxiety disorders), physical disorders (such as chronic fatigue syndrome), and s ...
and handing over of power to German Admiral Karl D├Čnitz in May of 1945, the Soviet troops conquered Berlin and accepted German surrender led by D├Čnitz. The last battles were fought as part of the Eastern Front which ended in the total surrender of all of Nazi GermanyŌĆÖs remaining armed forces
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
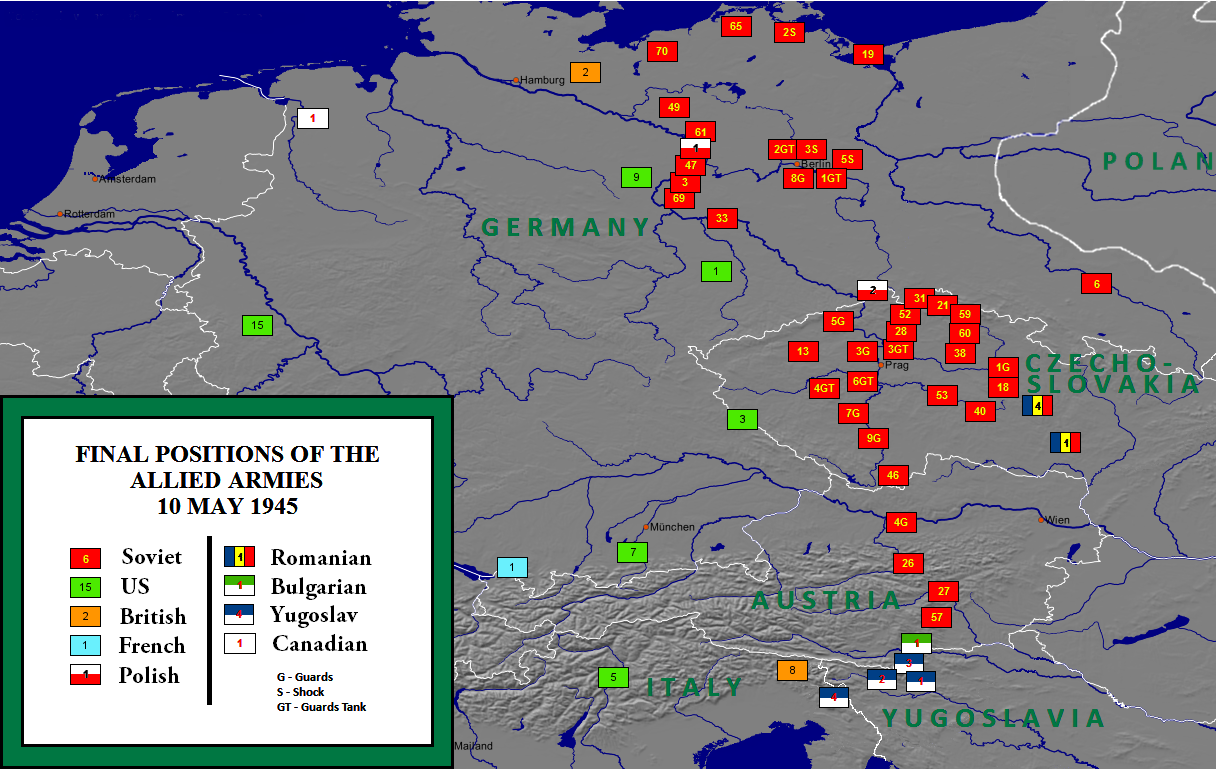
and the German surrender officially ended World War II in Europe, such as in the Courland Pocket from Army Group North in the Baltics lasting until 10 May 1945 and in Czechoslovakia during the Prague offensive
The Prague offensive (russian: ą¤čĆą░ąČčüą║ą░čÅ čüčéčĆą░č鹥ą│ąĖč湥čüą║ą░čÅ ąĮą░čüčéčāą┐ą░č鹥ą╗čīąĮą░čÅ ąŠą┐ąĄčĆą░čåąĖčÅ, Prazhskaya strategicheskaya nastupatel'naya operatsiya, lit=Prague strategic offensive) was the last major military ...
on 11 May 1945.
Final events before the end of the war in Europe
Red Army soldiers from the322nd Rifle Division
The 322nd Rifle Division was a standard Red Army rifle division during World War II. It is most notable for liberating Auschwitz concentration camp as part of the 60th Army on January 27, 1945, in the course of the Vistula-Oder offensive. Prior ...
liberated Auschwitz concentration camp
Auschwitz concentration camp ( (); also or ) was a complex of over 40 concentration and extermination camps operated by Nazi Germany in occupied Poland (in a portion annexed into Germany in 1939) during World War II and the Holocaust. It con ...
on 27 January 1945 at 15:00. Two hundred and thirty-one Red Army soldiers died in the fighting around Monowitz concentration camp, Birkenau, and Auschwitz I, as well as the towns of O┼øwi─Öcim and Brzezinka. For most of the survivors, there was no definite moment of liberation. After the death march away from the camp, the ''SS-Totenkopfverb├żnde
''SS-Totenkopfverb├żnde'' (SS-TV; ) was the ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) organization responsible for administering the Nazi concentration camps and extermination camps for Nazi Germany, among similar duties. While the ''Totenkopf'' was the univer ...
'' guards had left.
About 7,000 prisoners had been left behind, most of whom were seriously ill due to the effects of their imprisonment. Most of those left behind were middle-aged adults or children younger than 15. Red Army soldiers found 600 corpses, 370,000 men's suits, 837,000 articles of women's clothing, and seven tonnes (7.7 tons) of human hair. At Monowitz camp, there were about 800 survivors and the camp was liberated on 27 January by the Soviet 60th Army, part of the 1st Ukrainian Front.
Soldiers who were used to death were shocked by the Nazis' treatment of prisoners. Red Army general Vasily Petrenko, commander of the 107th Infantry Division, remarked, "I, who saw people dying every day, was shocked by the Nazis' indescribable hatred toward the inmates who had turned into living skeletons. I read about the Nazis' treatment of prisoners in various leaflets, but there was nothing about the Nazis' treatment of women, children, and old men. It was in Auschwitz that I found out about the fate of the Jews."
As soon as they arrived, the liberating forces, which contained the Polish Red Cross, helped survivors by organizing medical care and food; Red Army hospitals cared for 4,500 survivors. There were also efforts to document the camp. As late as June 1945, there were still 300 survivors at the camp who were too weak to be moved.
Allied forces begin to take large numbers of Axis prisoners: The total number of prisoners taken on the Western Front in April 1945 by the Western Allies was 1,500,000. April also witnessed the capture of at least 120,000 German troops by the Western Allies in the last campaign of the war in Italy.''The Times'', 1 May 1945, page 4 In the three to four months up to the end of April, over 800,000 German soldiers surrendered on the Eastern Front. In early April, the first Allied
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
-governed '' Rheinwiesenlagers'' were established in western Germany to hold hundreds of thousands of captured or surrendered Axis Forces personnel. Supreme Headquarters Allied Expeditionary Force
Supreme Headquarters Allied Expeditionary Force (SHAEF; ) was the headquarters of the Commander of Allied forces in north west Europe, from late 1943 until the end of World War II. U.S. General Dwight D. Eisenhower was the commander in SHAEF th ...
(SHAEF) reclassified all prisoners as Disarmed Enemy Forces
Disarmed Enemy Forces (DEF, less commonly, Surrendered Enemy Forces) was a US designation for soldiers who surrendered to an adversary after hostilities ended, and for those POWs who had already surrendered and were held in camps in occupied Ger ...
, not POW
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold prisoners of war ...
s (prisoners of war). The legal fiction
A legal fiction is a fact assumed or created by courts, which is then used in order to help reach a decision or to apply a legal rule. The concept is used almost exclusively in common law jurisdictions, particularly in England and Wales.
Deve ...
circumvented provisions under the Geneva Convention of 1929 on the treatment of former combatants. By October, thousands had died in the camps from starvation, exposure and disease.
 Liberation of Nazi concentration camps and refugees: Allied forces began to discover the scale of the Holocaust, confirming the findings of Pilecki's 1943 Report. The advance into Germany uncovered numerous Nazi concentration camps and forced labour facilities. Up to 60,000 prisoners were at Bergen-Belsen when it was liberated on 15 April 1945, by the British
Liberation of Nazi concentration camps and refugees: Allied forces began to discover the scale of the Holocaust, confirming the findings of Pilecki's 1943 Report. The advance into Germany uncovered numerous Nazi concentration camps and forced labour facilities. Up to 60,000 prisoners were at Bergen-Belsen when it was liberated on 15 April 1945, by the British 11th Armoured Division
The 11th Armoured Division was an armoured division of the British Army which was created in March 1941 during the Second World War. The division was formed in response to the unanticipated success of the German panzer divisions. The 11th Armou ...
."The 11th Armoured Division (Great Britain)"United States Holocaust Memorial Museum. Four days later troops from the American 42nd Infantry Division found
Dachau
,
, commandant = List of commandants
, known for =
, location = Upper Bavaria, Southern Germany
, built by = Germany
, operated by = ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS)
, original use = Political prison
, construction ...
. Allied troops forced the remaining SS guards to gather up the corpses and place them in mass graves. Due to the prisoners' poor physical condition, thousands continued to die after liberation. Captured SS guards were subsequently tried at Allied war crime tribunals where many were sentenced to death. Some Nazi guards and personnel were murdered outright upon the discovery of their crimes. However, up to 10,000 Nazi war criminals eventually fled Europe using ratlines such as ODESSA
Odesa (also spelled Odessa) is the third most populous city and municipality in Ukraine and a major seaport and transport hub located in the south-west of the country, on the northwestern shore of the Black Sea. The city is also the administrativ ...
.
German forces withdraw from Finland: On 25 April 1945, the last German troops withdrew from Finnish Lapland and made their way into occupied Norway. On 27 April 1945, the '' Raising the Flag on the Three-Country Cairn'' photograph was taken.
Mussolini is executed: On 25 April 1945, Italian partisans
The Italian resistance movement (the ''Resistenza italiana'' and ''la Resistenza'') is an umbrella term for the Italian resistance groups who fought the occupying forces of Nazi Germany and the fascist collaborationists of the Italian Soci ...
liberated Milan and Turin. On 27 April 1945, as Allied forces closed in on Milan, Italian dictator Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (; 29 July 188328 April 1945) was an Italian politician and journalist who founded and led the National Fascist Party. He was Prime Minister of Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 until his deposition in 194 ...
was captured by Italian partisans. It is disputed whether he was trying to flee from Italy to Switzerland (through the Spl├╝gen Pass), and was travelling with a German anti-aircraft battalion. On 28 April, Mussolini was executed in Giulino (a civil parish of Mezzegra); the other fascists captured with him were taken to Dongo and executed there. The bodies were then taken to Milan and hung up on the Piazzale Loreto of the city. On 29 April, Rodolfo Graziani
Rodolfo Graziani, 1st Marquis of Neghelli (; 11 August 1882 ŌĆō 11 January 1955), was a prominent Italian military officer in the Kingdom of Italy's ''Regio Esercito'' ("Royal Army"), primarily noted for his campaigns in Africa before and during ...
surrendered all Fascist Italian armed forces at Caserta. This included Army Group Liguria. Graziani was the Minister of Defence for Mussolini's Italian Social Republic
The Italian Social Republic ( it, Repubblica Sociale Italiana, ; RSI), known as the National Republican State of Italy ( it, Stato Nazionale Repubblicano d'Italia, SNRI) prior to December 1943 but more popularly known as the Republic of Sal├▓ ...
.


 Hitler dies by suicide: On 30 April 1945, as the Battle of Nuremberg and the Battle of Hamburg ended with American and British occupation, in addition to the
Hitler dies by suicide: On 30 April 1945, as the Battle of Nuremberg and the Battle of Hamburg ended with American and British occupation, in addition to the Battle of Berlin
The Battle of Berlin, designated as the Berlin Strategic Offensive Operation by the Soviet Union, and also known as the Fall of Berlin, was one of the last major offensives of the European theatre of World War II.
After the VistulaŌĆō ...
raging above him with the Soviets surrounding the city, along with his escape route cut off by the Americans, realizing that all was lost and not wishing to suffer Mussolini's fate, German dictator Adolf Hitler died by suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Mental disorders (including depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, personality disorders, anxiety disorders), physical disorders (such as chronic fatigue syndrome), and s ...
in his ''F├╝hrerbunker
The ''F├╝hrerbunker'' () was an air raid shelter located near the Reich Chancellery in Berlin, Germany. It was part of a subterranean bunker complex constructed in two phases in 1936 and 1944. It was the last of the F├╝hrer Headquarters ( ...
'' along with Eva Braun, his long-term partner whom he had married less than 40 hours earlier. In his will, Hitler dismissed '' Reichsmarschall'' Hermann G├Čring, his second-in-command and Interior minister
An interior minister (sometimes called a minister of internal affairs or minister of home affairs) is a cabinet official position that is responsible for internal affairs, such as public security, civil registration and identification, emergency ...
Heinrich Himmler after each of them separately tried to seize control of the crumbling remains of Nazi Germany. Hitler appointed his successors as follows; ''Gro├¤admiral'' Karl D├Čnitz
Karl D├Čnitz (sometimes spelled Doenitz; ; 16 September 1891 24 December 1980) was a German admiral who briefly succeeded Adolf Hitler as head of state in May 1945, holding the position until the dissolution of the Flensburg Government follo ...
as the new '' Reichspr├żsident'' ("President of Germany") and Joseph Goebbels
Paul Joseph Goebbels (; 29 October 1897 ŌĆō 1 May 1945) was a German Nazi politician who was the ''Gauleiter'' (district leader) of Berlin, chief propagandist for the Nazi Party, and then Reich Minister of Propaganda from 1933 to 19 ...
as the new '' Reichskanzler'' (Chancellor of Germany). However, Goebbels died by suicide the next day, leaving D├Čnitz as the sole leader of Germany.
German forces in Italy surrender: On 29 April, the day before Hitler died, Oberstleutnant Schweinitz and Sturmbannf├╝hrer Wenner, plenipotentiaries for Generaloberst Heinrich von Vietinghoff and SS Obergruppenf├╝hrer Karl Wolff
Karl Friedrich Otto Wolff (13 May 1900 ŌĆō 17 July 1984) was a German SS functionary who served as Chief of Personal Staff Reichsf├╝hrer-SS (Heinrich Himmler) and an SS liaison to Adolf Hitler during World War II. He ended the war as the Supre ...
, signed a surrender document at Caserta after prolonged unauthorised secret negotiations with the Western Allies, which were viewed with great suspicion by the Soviet Union as trying to reach a separate peace. In the document, the Germans agreed to a ceasefire and surrender of all the forces under the command of Vietinghoff on 2 May at 2 pm. Accordingly, after some bitter wrangling between Wolff and Albert Kesselring in the early hours of 2 May, nearly 1,000,000 men in Italy and Austria surrendered unconditionally to British Field Marshal Sir Harold Alexander on 2 May at 2 pm.
German forces in Berlin surrender: The Battle of Berlin
The Battle of Berlin, designated as the Berlin Strategic Offensive Operation by the Soviet Union, and also known as the Fall of Berlin, was one of the last major offensives of the European theatre of World War II.
After the VistulaŌĆō ...
ended on 2 May. On that date, ''General der Artillerie'' Helmuth Weidling, the commander of the Berlin Defense Area, unconditionally surrendered the city to General Vasily Chuikov of the Red Army. On the same day the officers commanding the two armies of Army Group Vistula
Army Group Vistula () was an Army Group of the ''Wehrmacht'', formed on 24 January 1945. It lasted for 105 days, having been put together from elements of Army Group A (shattered in the Soviet Vistula-Oder Offensive), Army Group Centre (similarl ...
north of Berlin, (General Kurt von Tippelskirch, commander of the German 21st Army and General Hasso von Manteuffel, commander of Third Panzer Army
The 3rd Panzer Army (german: 3. Panzerarmee) was a German armoured formation during World War II, formed from the 3rd Panzer Group on 1 January 1942.
3rd Panzer Group
The 3rd Panzer Group (german: Panzergruppe 3) was formed on 16 November ...
), surrendered to the Western Allies. 2 May is also believed to have been the day when Hitler's deputy Martin Bormann
Martin Ludwig Bormann (17 June 1900 ŌĆō 2 May 1945) was a German Nazi Party official and head of the Nazi Party Chancellery. He gained immense power by using his position as Adolf Hitler's private secretary to control the flow of information ...
died, from the account of Artur Axmann who saw Bormann's corpse in Berlin near the Lehrter Bahnhof railway station after encountering a Soviet Red Army patrol. Lehrter Bahnhof is close to where the remains of Bormann, confirmed as his by a DNA test in 1998, were unearthed on 7 December 1972.
German forces in North West Germany, Denmark, and the Netherlands surrender: On 4 May 1945, the British Field Marshal
Field marshal (or field-marshal, abbreviated as FM) is the most senior military rank, ordinarily senior to the general officer ranks. Usually, it is the highest rank in an army and as such few persons are appointed to it. It is considered as ...
Bernard Montgomery
Field Marshal Bernard Law Montgomery, 1st Viscount Montgomery of Alamein, (; 17 November 1887 ŌĆō 24 March 1976), nicknamed "Monty", was a senior British Army officer who served in the First World War, the Irish War of Independence and t ...
took the unconditional military surrender at L├╝neburg from ''Generaladmiral'' Hans-Georg von Friedeburg, and General Eberhard Kinzel, of all German forces "in Holland ic in northwest Germany including the Frisian Islands and Heligoland and all other islands, in Schleswig-Holstein, and in DenmarkŌĆ” includ ngall naval ships in these areas", at the Timeloberg
Wendisch Evern is a municipality in the district of L├╝neburg, in Lower Saxony, Germany.
Recent history (Second World War)
On 4 May 1945 on the ''Timeloberg'' hill at the edge of Deutsch Evern a German delegation under the command of Hans-Geo ...
on L├╝neburg Heath
L├╝neburg Heath (german: L├╝neburger Heide) is a large area of heath, geest, and woodland in the northeastern part of the state of Lower Saxony in northern Germany. It forms part of the hinterland for the cities of Hamburg, Hanover and Bremen a ...
; an area between the cities of Hamburg, Hanover and Bremen
Bremen (Low German also: ''Breem'' or ''Br├żm''), officially the City Municipality of Bremen (german: Stadtgemeinde Bremen, ), is the capital of the German state Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (''Freie Hansestadt Bremen''), a two-city-state consis ...
. The number of German land, sea and air forces involved in this surrender amounted to 1,000,000 men.
On 5 May, ''Gro├¤admiral'' D├Čnitz ordered all U-boats to cease offensive operations and return to their bases.
At 16:00 on 5 May, German '' Oberbefehlshaber Niederlande'' supreme commander '' Generaloberst'' Johannes Blaskowitz surrendered to I Canadian Corps commander Lieutenant-General
Lieutenant general (Lt Gen, LTG and similar) is a three-star military rank (NATO code OF-8) used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages, where the title of lieutenant general was held by the second-in-command on the ...
Charles Foulkes in the Dutch town of Wageningen, in the presence of Prince Bernhard of the Netherlands (acting as commander-in-chief of the Dutch Interior Forces).Ron Goldstein Field Marshal Keitel's surrender
' BBC additional comment b
Peter ŌĆō WW2 Site Helper
/ref> German forces in Bavaria surrender: At 14:30 on 5 May 1945, General Hermann Foertsch surrendered all forces between the
Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, ─īechy ; ; hsb, ─ī─øska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
n mountains and the Upper Inn river to the American General Jacob L. Devers, commander of the American 6th Army Group
The 6th United States Army Group was an Allied Army Group that fought in the European Theater of Operations during World War II. Made up of field armies from both the United States Army and the French Army, it fought in France, Germany, Austr ...
.
Central Europe: On 5 May 1945, the Czech resistance started the Prague uprising
The Prague uprising ( cs, Pra┼Šsk├® povst├Īn├Ł) was a partially successful attempt by the Czech resistance movement to liberate the city of Prague from German occupation in May 1945, during the end of World War II. The preceding six years of o ...
. The following day, the Soviets launched the Prague Offensive
The Prague offensive (russian: ą¤čĆą░ąČčüą║ą░čÅ čüčéčĆą░č鹥ą│ąĖč湥čüą║ą░čÅ ąĮą░čüčéčāą┐ą░č鹥ą╗čīąĮą░čÅ ąŠą┐ąĄčĆą░čåąĖčÅ, Prazhskaya strategicheskaya nastupatel'naya operatsiya, lit=Prague strategic offensive) was the last major military ...
. In Dresden, ''Gauleiter'' Martin Mutschmann
Martin Mutschmann (9 March 1879 – 14 February 1947) was the Nazi Regional Leader (''Gauleiter'') of the state of Saxony ('' Gau Saxony'') during the time of the Third Reich.
Early years
Born in Hirschberg on the Saale in the Principality ...
let it be known that a large-scale German offensive on the Eastern Front was about to be launched. Within two days, Mutschmann abandoned the city but was captured by Soviet troops while trying to escape.
Hermann G├Čring's surrender: On 6 May, ''Reichsmarshall'' and Hitler's second-in-command, Hermann G├Čring, surrendered to General Carl Spaatz
Carl Andrew Spaatz (born Spatz; June 28, 1891 ŌĆō July 14, 1974), nicknamed "Tooey", was an American World War II general. As commander of Strategic Air Forces in Europe in 1944, he successfully pressed for the bombing of the enemy's oil product ...
, who was the commander of the operational United States Air Forces in Europe, along with his wife and daughter at the Germany- Austria border. He was by this time the most senior Nazi official still alive.
German forces in Breslau surrender: At 18:00 on 6 May, General Hermann Niehoff __NOTOC__
Hermann Niehoff (3 April 1897 ŌĆō 5 November 1980) was a German general during World War II. In 1944, he was a liuetenant general and commander of Heersgebeit Sudfrankreich (Army Group Southern France) facing the US/French invasion of ...
, the commandant of Breslau, a 'fortress' city surrounded and besieged for months, surrendered to the Soviets.
Jodl and Keitel surrender all German armed forces unconditionally: Thirty minutes after the fall of "'' Festung Breslau''" (''Fortress Breslau''), General Alfred Jodl
Alfred Josef Ferdinand Jodl (; 10 May 1890 ŌĆō 16 October 1946) was a German ''Generaloberst'' who served as the chief of the Operations Staff of the '' Oberkommando der Wehrmacht'' ŌĆō the German Armed Forces High Command ŌĆō throughout World ...
arrived in Reims
Reims ( , , ; also spelled Rheims in English) is the most populous city in the French department of Marne, and the 12th most populous city in France. The city lies northeast of Paris on the Vesle river, a tributary of the Aisne.
Founded by ...
and, following D├Čnitz's instructions, offered to surrender all forces fighting the Western Allies. This was exactly the same negotiating position that von Friedeburg had initially made to Montgomery, and like Montgomery, the Supreme Allied Commander
Supreme Allied Commander is the title held by the most senior commander within certain multinational military alliances. It originated as a term used by the Allies during World War I, and is currently used only within NATO for Supreme Allied Comm ...
, General Dwight D. Eisenhower, threatened to break off all negotiations unless the Germans agreed to a complete unconditional surrender to all the Allies on all fronts. Eisenhower explicitly told Jodl that he would order western lines closed to German soldiers, thus forcing them to surrender to the Soviets. Jodl sent a signal to D├Čnitz, who was in Flensburg
Flensburg (; Danish, Low Saxon: ''Flensborg''; North Frisian: ''Flansborj''; South Jutlandic: ''Flensborre'') is an independent town (''kreisfreie Stadt'') in the north of the German state of Schleswig-Holstein. Flensburg is the centre of the ...
, informing him of Eisenhower's declaration. Shortly after midnight, D├Čnitz, accepting the inevitable, sent a signal to Jodl authorizing the complete and total surrender of all German forces.
 Channel Islanders were informed about the German surrender after: At 10:00 on 8 May, the
Channel Islanders were informed about the German surrender after: At 10:00 on 8 May, the Channel Island
The Channel Islands ( nrf, Îles d'la Manche; french: îles Anglo-Normandes or ''îles de la Manche'') are an archipelago in the English Channel, off the French coast of Normandy. They include two Crown Dependencies: the Bailiwick of Jersey, ...
ers were informed by the German authorities that the war was over. British prime minister Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 Winston Churchill in the Second World War, dur ...
made a radio broadcast at 15:00 during which he announced: "Hostilities will end officially at one minute after midnight tonight, but in the interests of saving lives the 'Cease fire' began yesterday to be sounded all along the front, and our dear Channel Islands are also to be freed today."During the summers of World War II, Britain was on British Double Summer Time
During British Summer Time (BST), civil time in the United Kingdom is advanced one hour forward of Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), in effect changing the time zone from UTC┬▒00:00 to UTC+01:00, so that mornings have one hour less daylight, and ev ...
which meant that the country was ahead of CET time by one hour. This means that the surrender time in the UK was "effective from 0001 hours on May 9RAF Site Diary 7/8 May
At 02:41 on the morning of 7 May, at SHAEF headquarters in Reims, France, the chief-of-staff of the German Armed Forces High Command, General Alfred Jodl, signed an unconditional surrender document for all German forces to the Allies. General Franz B├Čhme announced the unconditional surrender of German troops in Norway on 7 May. It included the phrase "All forces under German control to cease active operations at 2301 hours Central European Time on May 8, 1945." The next day, Field Marshal Wilhelm Keitel and other German OKW representatives travelled to Berlin, and shortly before midnight signed another document of unconditional surrender, again surrendering to all the Allied forces, this time in the presence of Marshal Georgi Zhukov and representatives of SHAEF. The signing ceremony took place in a former German Army Engineering School in the Berlin district of
Karlshorst
Karlshorst (, ; ; literally meaning ''Karl's nest'') is a locality in the borough of Lichtenberg in Berlin. Located there are a harness racing track and the Hochschule f├╝r Technik und Wirtschaft Berlin (''HTW''), the largest University of Applied ...
; it now houses the German-Russian Museum Berlin-Karlshorst.
Aftermath of the war
VE-Day: Following news of the German surrender, spontaneous celebrations erupted all over the world on 7 May, including in Western Europe and the United States. As the Germans officially set the end of operations for 2301 Central European Time on 8 May, that day is celebrated across Europe as V-E Day. Most of the former Soviet Union celebrates Victory Day on 9 May, as the end of operations occurred after midnight Moscow Time. German units cease fire: Although the military commanders of most German forces obeyed the order to surrender issued by the '' Oberkommando der Wehrmacht'' (OKW)ŌĆöthe German Armed Forces High CommandŌĆönot all commanders did so. The largest contingent wasArmy Group Centre
Army Group Centre (german: Heeresgruppe Mitte) was the name of two distinct strategic German Army Groups that fought on the Eastern Front in World War II. The first Army Group Centre was created on 22 June 1941, as one of three German Army fo ...
under the command of ''Generalfeldmarschall'' Ferdinand Sch├Črner, who had been promoted to Commander-in-Chief of the Army on 30 April in Hitler's last will and testament. On 8 May, Sch├Črner deserted his command and flew to Austria; the Soviet Army sent overwhelming force against Army Group Centre in the Prague Offensive
The Prague offensive (russian: ą¤čĆą░ąČčüą║ą░čÅ čüčéčĆą░č鹥ą│ąĖč湥čüą║ą░čÅ ąĮą░čüčéčāą┐ą░č鹥ą╗čīąĮą░čÅ ąŠą┐ąĄčĆą░čåąĖčÅ, Prazhskaya strategicheskaya nastupatel'naya operatsiya, lit=Prague strategic offensive) was the last major military ...
, forcing many of the German units in there to capitulate by 11 May. The other units of the Army Group which did not surrender on 8 May were forced to surrender.
* On, 9 May, the Second Army, under the command of General von Saucken, on the Heiligenbeil and Danzig beachheads, on the Hel Peninsula in the Vistula delta surrendered; as did the forces on the Greek islands; and the garrisons of most of the last Atlantic pockets
In World War II, the Atlantic pockets were locations along the coasts of the Netherlands, Belgium and France chosen as strongholds by the occupying German forces, to be defended as long as possible against land attack by the Allies.
The location ...
in France, in Dunkirk
Dunkirk (french: Dunkerque ; vls, label=French Flemish, Duunkerke; nl, Duinkerke(n) ; , ;) is a commune in the department of Nord in northern France.La Rochelle (after the Allied siege).
* The Atlantic Pocket of Lorient surrendered on 10 May.
* The Atlantic Pocket of  The
The 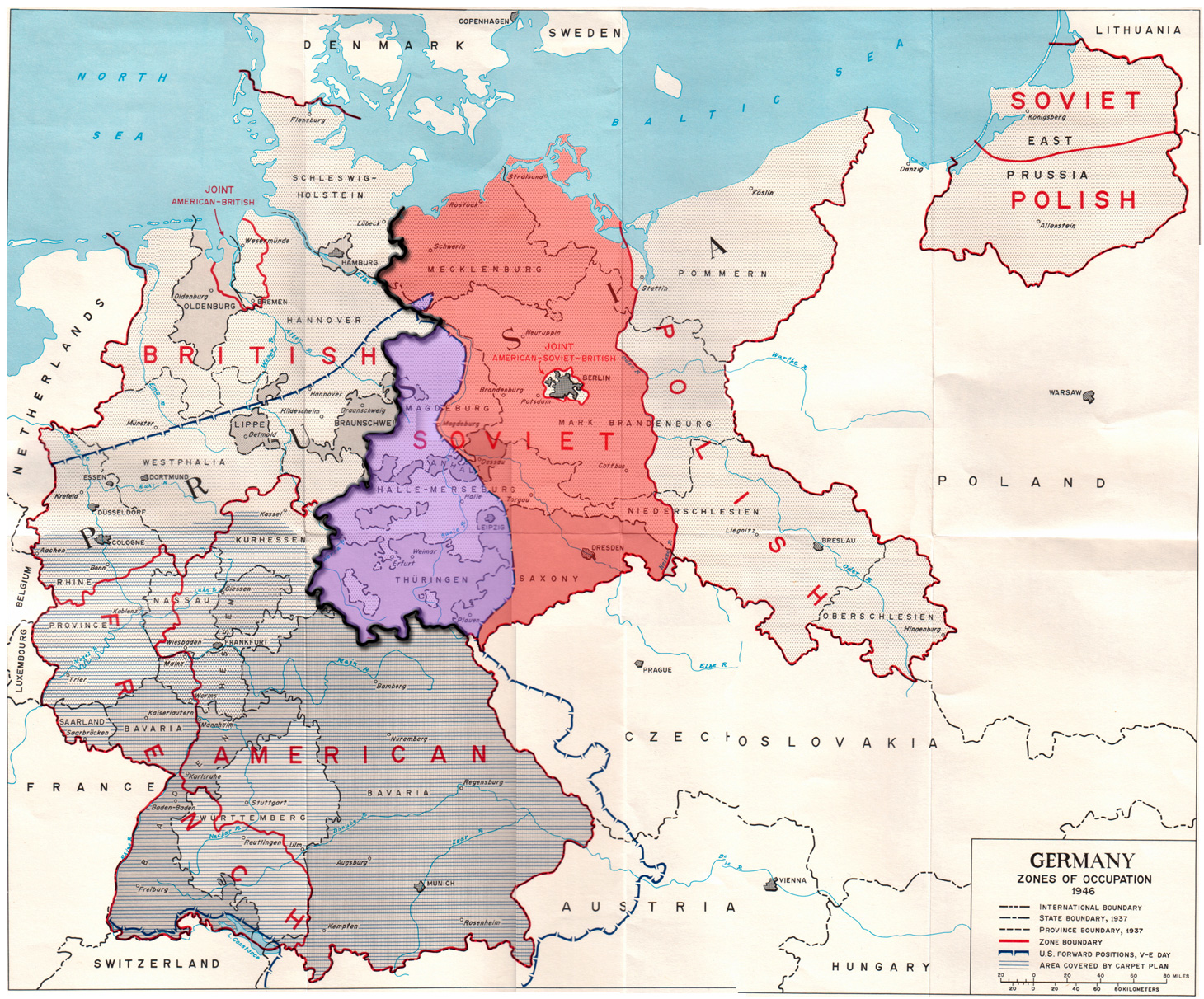
"Spreading Hesitation"
''Time''. 7 February 1955.
"The full authority of a sovereign state" was granted to the Federal Republic of Germany on 5 May 1955 under the terms of the BonnŌĆōParis conventions.
The treaty ended the military occupation of West German territory, but the three occupying powers retained some special rights, e.g. vis-├Ā-vis West Berlin.
The Treaty on the Final Settlement with Respect to Germany was signed following the 1990 
Deutsche Welle special coverage of the end of World War II
Ćöfeatures a global perspective.
On this Day 7 May 1945: Germany signs unconditional surrender
Account of German surrender
BBC * Charles Kiley ( Stars and Stripes Staff Writer
Details of the Surrender Negotiations ''This Is How Germany Gave Up''
* ttp://english.pobediteli.ru/ Multimedia map of the war(1024x768 & Macromedia Flash Plugin 7.x)
Saint-Nazaire
Saint-Nazaire (; ; Gallo: ''Saint-Naz├©re/Saint-Nazaer'') is a commune in the Loire-Atlantique department in western France, in traditional Brittany.
The town has a major harbour on the right bank of the Loire estuary, near the Atlantic Ocean ...
surrendered on 11 May.
* The Battle of Slivice
The Battle of Slivice was the last large World War II battle in the area of the Czech lands. During 11ŌĆō12 May 1945, German troops, trying to surrender to nearby American troops rather than the USSR, defended themselves against local partisans ...
, the last battle in occupied Czechoslovakia, occurred on 12 May.
* On 13 May, the Red Army halted all offensives in Europe. Isolated pockets of resistance in Czechoslovakia were mopped up by this date.
* The garrison on Alderney
Alderney (; french: Aurigny ; Auregnais: ) is the northernmost of the inhabited Channel Islands. It is part of the Bailiwick of Guernsey, a British Crown dependency. It is long and wide.
The island's area is , making it the third-largest ...
, one of the Channel Islands occupied by the Germans, surrendered on 16 May, one week after the garrisons on Guernsey
Guernsey (; Guern├®siais: ''Guern├®si''; french: Guernesey) is an island in the English Channel off the coast of Normandy that is part of the Bailiwick of Guernsey, a British Crown Dependency.
It is the second largest of the Channel Islands ...
and Jersey had surrendered on 9 May and those on Sark on 10 May.
* A military engagement took place in Yugoslavia (today's Slovenia), on 14 and 15 May, known as the Battle of Poljana.
* The fighting during the Georgian uprising on Texel
The Georgian uprising on Texel ( nl, Opstand der Georgi├½rs) (5 April 1945 ŌĆō 20 May 1945) was an insurrection by the 882nd Infantry Battalion ''K├Čnigin Tamara'' (Queen Tamar or ''Tamara'') of the Georgian Legion of the German Army stationed o ...
in the Netherlands lasted until 20 May.
* The last battle in Europe, the Battle of Od┼Šak
The Battle of Od┼Šak was the last battle of World War II in Europe. The battle began on 19 April 1945 and lasted until 25 May 1945, 17 days after the end of the war in Europe. The combatants were the Armed Forces of the Independent State of Cro ...
between the Yugoslav Army and the Croatian Armed Forces, concluded on 25 May. The remaining Croatian soldiers escaped to the forest.
* A small group of German soldiers, deployed on Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range ...
in Operation Haudegen
Operation Haudegen ( peration Broadsword was the name of a Nazi Germany, German operation during the Second World War to establish meteorological stations on Svalbard. In September 1944, the submarine ''U-307'' and the supply ship ''Carl J. ...
to establish and man a weather station there, lost radio contact in May 1945; they surrendered to some Norwegian seal hunters on 4 September, two days after Japan formally surrendered.
Debellation: At the time the Allied powers assumed that a debellation had occurred (the end of a war caused by the complete destruction of a hostile state), and their actions during the immediate post war period were based on that legal premise (however the German government's legal position during and after the reunification of Germany
German reunification (german: link=no, Deutsche Wiedervereinigung) was the process of re-establishing Germany as a united and fully sovereign state, which took place between 2 May 1989 and 15 March 1991. The day of 3 October 1990 when the Ge ...
is that the state remained in existence although moribund in the immediate post war period).
D├Čnitz government ordered dissolved by Eisenhower: Karl D├Čnitz continued to act as if he were the German head of state, but his Flensburg government (so called because it was based at Flensburg in northern Germany and controlled only a small area around the town), was not recognized by the Allies. On 12 May an Allied liaison team arrived in Flensburg and took quarters aboard the passenger ship ''Patria''. The liaison officers and the Supreme Allied Headquarters soon realized that they had no need to act through the Flensburg government and that its members should be arrested. On 23 May, acting on SHAEF's orders and with the approval of the Soviets, American Major General Rooks summoned D├Čnitz aboard the ''Patria'' and communicated to him that he and all the members of his Government were under arrest and that their government was dissolved. The Allies had a problem because they realized that although the German armed forces had surrendered unconditionally, SHAEF had failed to use the document created by the " European Advisory Commission" (EAC) and so there had been no formal surrender by the civilian German government. This was considered a very important issue, because just as the civilian, but not military, surrender in 1918 had been used by Hitler to create the "stab in the back
The stab-in-the-back myth (, , ) was an antisemitic conspiracy theory that was widely believed and promulgated in Germany after 1918. It maintained that the Imperial German Army did not lose World War I on the battlefield, but was instead ...
" argument, the Allies did not want to give any future hostile German regime a legal argument to resurrect an old quarrel.
On 20 September 1945, the Allied Control Council
The Allied Control Council or Allied Control Authority (german: Alliierter Kontrollrat) and also referred to as the Four Powers (), was the governing body of the Allied Occupation Zones in Germany and Allied-occupied Austria after the end of Wo ...
passed its Control Council Law No. 1 - Repealing of Nazi Laws
The Control Council Law No. 1 ŌĆō Repealing of Nazi Laws (, short form: ''Kontrollratsgesetz Nr. 1'') was a law enacted by the Allied Control Council for post-World War II Germany on 20 September 1945.
Description
It repealed numerous pieces of ...
, which repealed numerous pieces of legislation enacted by the national-socialist regime, putting a ''de jure'' end to the Government of Nazi Germany
The government of Nazi Germany was totalitarian, run by the Nazi Party in Germany according to the F├╝hrerprinzip through the dictatorship of Adolf Hitler. Nazi Germany began with the fact that the Enabling Act was enacted to give Hitler's gover ...
. Incidentally, this law should have theoretically reestablished the Weimar Constitution
The Constitution of the German Reich (german: Die Verfassung des Deutschen Reichs), usually known as the Weimar Constitution (''Weimarer Verfassung''), was the constitution that governed Germany during the Weimar Republic era (1919ŌĆō1933). The c ...
, however this constitution stayed irrelevant on the grounds of the powers of the Allied Control Council acting as occupying forces. On 10 October 1945, Control Council Law No. 2 was also passed, formally abolishing all national socialist organisations.
Declaration Regarding the Defeat of Germany and the Assumption of Supreme Authority by Allied Powers was signed by the four Allies on 5 June. It included the following:
 The
The Potsdam Agreement
The Potsdam Agreement (german: Potsdamer Abkommen) was the agreement between three of the Allies of World War II: the United Kingdom, the United States, and the Soviet Union on 1 August 1945. A product of the Potsdam Conference, it concerned th ...
was signed on 1 August 1945. In connection with this, the leaders of the United States, Britain and the Soviet Union planned the new postwar German government, resettled war territory boundaries, ''de facto'' annexed a quarter of pre-war Germany situated east of the Oder-Neisse line, and mandated and organized the expulsion of the millions of Germans who remained in the annexed territories and elsewhere in the east. They also ordered German demilitarization, denazification
Denazification (german: link=yes, Entnazifizierung) was an Allied initiative to rid German and Austrian society, culture, press, economy, judiciary, and politics of the Nazi ideology following the Second World War. It was carried out by remov ...
, industrial disarmament and settlements of war reparations. But, as France (at American insistence) had not been invited to the Potsdam Conference, so the French representatives on the Allied Control Council subsequently refused to recognise any obligation to implement the Potsdam Agreement; with the consequence that much of the programme envisaged at Potsdam, for the establishment of a German government and state adequate for accepting a peace settlement, remained a dead letter.

Operation Keelhaul
Operation Keelhaul was a forced repatriation of Russian civilians (non-Soviet citizens) and Soviet citizens to the Soviet Union. While forced repatriation focused on Soviet Armed Forces POWs of Germany and Russian Liberation Army members, it inclu ...
began the Allies' forced repatriation of displaced persons, families, anti-communists, White Russians, former Soviet Armed Forces POW
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold prisoners of war ...
s, foreign slave workers, soldier volunteers and Cossacks
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, koz├Īkok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, ą║ąŠąĘą░╠üą║ąĖ, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: ą║ą░ąĘą░ą║ąĖ╠ü or ...
, and Nazi collaborators to the Soviet Union. Between 14 August 1946 and 9 May 1947, up to five million people were forcibly handed over to the Soviets. On return, most deportees faced imprisonment or execution; on some occasions the NKVD began killing people before Allied troops had departed from the rendezvous points.
The Allied Control Council
The Allied Control Council or Allied Control Authority (german: Alliierter Kontrollrat) and also referred to as the Four Powers (), was the governing body of the Allied Occupation Zones in Germany and Allied-occupied Austria after the end of Wo ...
was created to effect the Allies' assumed supreme authority over Germany, specifically to implement their assumed joint authority over Germany. On 30 August, the Control Council constituted itself and issued its first proclamation, which informed the German people of the council's existence and asserted that the commands and directives issued by the Commanders-in-Chief in their respective zones were not affected by the establishment of the council.
Cessation of formal hostilities and peace treaties
Cessation of hostilities between the United States and Germany was proclaimed on 13 December 1946 by US President Truman. The Paris Peace Conference ended on 10 February 1947 with the signing ofpeace treaties
A peace treaty is an agreement between two or more hostile parties, usually countries or governments, which formally ends a state of war between the parties. It is different from an armistice, which is an agreement to stop hostilities; a surre ...
by the wartime Allies with the former European Axis powers ( Italy, Romania, Hungary and Bulgaria) and their co-belligerent ally Finland.
The Federal Republic of Germany, which had been founded on 23 May 1949 (when its Basic Law was promulgated), had its first government formed on 20 September 1949 while the German Democratic Republic was formed on 7 October.
End of state of war with Germany was declared by many former Western Allies from 1950. In the Petersberg Agreement of 22 November 1949, it was noted that the West German government wanted an end to the state of war, but the request could not be granted. The US state of war with Germany was being maintained for legal reasons, and though it was softened somewhat it was not suspended since "the US wants to retain a legal basis for keeping a US force in Western Germany".
At a meeting for the foreign ministers of France, the UK, and the US in New York from 12 September ŌĆō 19 December 1950, it was stated that among other measures to strengthen West Germany's position in the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
that the western allies would "end by legislation the state of war with Germany". In 1951, many former Western Allies did end their state of war with Germany: Australia (9 July), Canada, Italy, New Zealand, the Netherlands (26 July), South Africa, the United Kingdom (9 July), and the United States (19 October). The state of war between Germany and the Soviet Union was ended in early 1955.''Time''. 7 February 1955.
German reunification
German reunification (german: link=no, Deutsche Wiedervereinigung) was the process of re-establishing Germany as a united and fully sovereign state, which took place between 2 May 1989 and 15 March 1991. The day of 3 October 1990 when the Ge ...
, whereby the Four Powers renounced all rights they formerly held in the newly single country, including Berlin. The treaty came into force on 15 March 1991. Under the terms of the Treaty, the Allies were allowed to keep troops in Berlin until the end of 1994 (articles 4 and 5). In accordance with the Treaty, occupying troops were withdrawn by that deadline.

See also
* End of World War II in Asia *Aftermath of World War II
The aftermath of World War II was the beginning of a new era started in late 1945 (when World War II ended) for all countries involved, defined by the decline of all colonial empires and simultaneous rise of two superpowers; the Soviet Union (US ...
* Allied Commission
Following the termination of hostilities in World War II, the Allies were in control of the defeated Axis countries. Anticipating the defeat of Germany and Japan, they had already set up the European Advisory Commission and a proposed Far Easter ...
s
* Council of Foreign Ministers
* German Instrument of Surrender
* Liberation of France
* Line of contact
* Surrender of Japan
The surrender of the Empire of Japan in World War II was announced by Emperor Hirohito on 15 August and formally signed on 2 September 1945, bringing the war's hostilities to a close. By the end of July 1945, the Imperial Japanese Navy ...
* Western betrayal
* German prisoners of war in northwest Europe
More than 2.8 million German soldiers surrendered on the Western Front between D-Day (June 6, 1944) and the end of April 1945; 1.3 million between D-Day and March 31, 1945;2,055,575 German soldiers surrendered between D-Day and April 16, 1945, ' ...
Notes
References
Citations
Sources
* * * *Further reading
Deutsche Welle special coverage of the end of World War II
Ćöfeatures a global perspective.
On this Day 7 May 1945: Germany signs unconditional surrender
Account of German surrender
BBC * Charles Kiley ( Stars and Stripes Staff Writer
Details of the Surrender Negotiations ''This Is How Germany Gave Up''
* ttp://english.pobediteli.ru/ Multimedia map of the war(1024x768 & Macromedia Flash Plugin 7.x)
External links
* * {{Authority control 1945 in military history 1945 in Europe European theatre of World War II Military history of Germany during World War II Chronology of World War II